What is categorical vs numerical data?
TL;DR numerical data refers to numbers while categorical data is basically everything else.
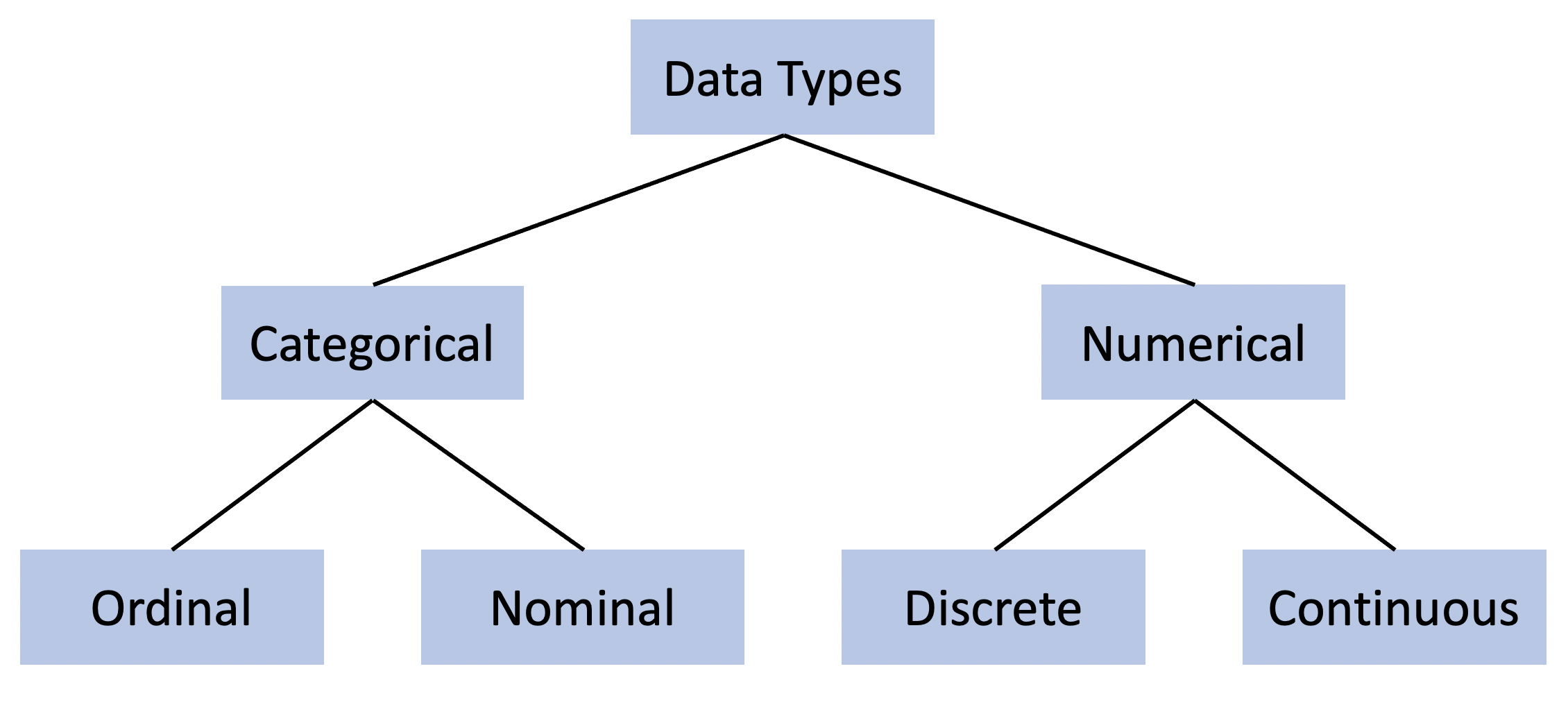
Categorical data
Categorical data is any data that can be place in a particular category based on its name or label. For example, if I survey 100 people at a boba shop and ask them what sort of drink they ordered the data I am recording is categorical. From this data, each person provides exactly one response making their answer mutually exclusive.
Categorical data can be further broken down into ordinal and nominal data.
- Ordinal data
- The easiest way to think about ordinal data is that is “score data”.
- If I asked you “On a scale of 1-10, how much do you like using this website?” Your response would be classified as ordinal data.
- Nominal data
- Nominal data is just name data.
- The example given above about the drinks ordered from a boba shop is an example of nominal data.
Numerical data
Numerical data is just numbers in their pure form. They are not being used to rank anything and they are not being used as descriptors. For example, if I measure the time it takes for a drop of paint to dry, that would be numerical data. If I measure the time it takes for a blade of grass to grow 1 mm; that would also be numerical data.
Much like categorial data, numerical data can also occur in two forms: continuous and discrete data.
- Discrete data
- The best way to describe discrete data is to think of it as countable data, like, “How dogs did I see at the park today?”
- 99.9% of the time you are going to respond with a whole number (in the case where you do not, that situation is not going to be solved with some basic statistics).
- Continuous data
- Where discrete data is typically an integer, count data is a measurement where the value can be any real number.
- That number can be 1 or 1.23 or 1.23456789.
Within continuous data there are two additional categories: interval and ratio data.
- Interval data
- Data that can be measured on a scale like the length of one’s left foot or the mass of one’s right thumb.
- Ratio data
- Data that is measured relative to a “true zero”.
- For example, how much above or below is your population’s body temperature compared to the normal body temperature of 98.6 degrees fahrenheit.